Precision Casting Patterns From RapidProtoCasting®
Casting Patterns For Production of Precision Castings in Cobalt-Chrome, Titanium, Copper, Stainless Steel and Inconel Alloys by RapidProtoCasting
Rapid prototypes, machined patterns, injected wax patterns and injected plastic patterns can all be used in RapidProtoCasting’s lost wax investment casting process.
RAPID PROTOTYPE CASTING PATTERNS
RapidProtoCasting has in-house rapid prototype capability and we work with rapid prototype service bureaus to create precision rapid prototypes for prototype castings and low volume castings. Rapid prototypes are fully inspected and measured to ensure the necessary casting quality and dimensions. Casting designs with large areas of thin walls may not be compatible with rapid prototype technologies and for some designs plastic injection tooling may be necessary for prototype castings and low-volume casting production. RapidProtoCasting can process all types of rapid prototype patterns including:
- Solidscape and Sanders
- 3D Systems SLA solid and QuickCast
- Objet Eden
- Envisiontec Perfactory
MACHINED CASTING PATTERNS
Using machined plastic parts as investment casting patterns can be an effective solution for low-volumes of larger parts and moderate volumes of small parts. As-machined CNC parts can often be used to produce castings with larger tolerances and rougher surface finish requirements.
INJECTED CASTING PATTERNS
RapidProtoCasting works with toolmakers and plastic injection companies to produce precision wax and plastic patterns for low-volume and moderate-volume castings, typically 50 to 50,000 parts. Casting designs that cannot be tooled (injected in one piece) can be injected as multiple parts and assembled to meet finished casting surface finish and dimensional requirements.
Wax Injected Patterns are used for castings with
- Thick Walls: wall thicknesses greater than 0.04″ (1.0mm).
- Larger Castings: typically with all extents larger than 0.25″ (6mm).
- Larger Tolerance Castings: greater than +/- 0.020 (0,5mm).
- Rougher Surface Castings: surface finish greater than 125 Ra (3.2 Rz) Wax injection tooling can be fabricated with as-machined cavities at lower cost if permitted by the required surface finish.
Plastic Injected Patterns are used to produce
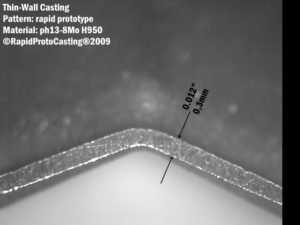
- Thin Wall Castings with wall thicknesses less than 0.04″ (1.0mm).
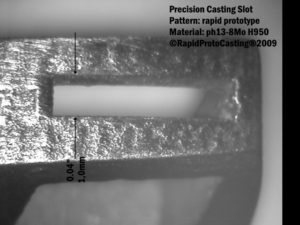
- Precision Castings where tolerances of 0.002″ (0.05mm) are required or process capability is required for tolerances less than 0.006″ (0.15mm).
- Small Castings where handling of brittle wax patterns may not be cost effective or efficient.
- Complex Castings requiring superior surface finish.
WAX INJECTION TOOLING
is used when cast part quantities make the investment in tooling economical compared to low-volume use of rapid prototype or machined patterns. Wax injection tooling can be fabricated from silicon, rubber, epoxy, epoxy in an aluminum shell, machined aluminum and machined steel. The selection of material is influenced by the total quantity of patterns required over the life of the tool, the dimensional tolerances required for the wax patterns, the complexity of the part and the tooling necessary to reproduce the part design properly, the time available for fabricating the tooling, the expected need to modify or adjust the tooling and the available budget. The typical process includes:
- Protocasting production of prototype quantities of finished castings and adjustment of the rapid prototype size and features to produce acceptable finished castings.
- CAD Modeling of the final pattern design and size including gating required for wax injection and casting.
- Design of wax injection tooling including slides, inserts, pickouts and cooling.
- Fabrication of the wax injection tool with extra stock (“metal safe”) to provide opportunities for final adjustment.
- Development of wax injection process to ensure adequate fill and surface finish.
- Injection of sample wax patterns and measurement of the sample patterns to confirm the dimensions of the cooled wax after removal from the tool.
- Investment casting of sample parts and measurement of the sample casting dimensions.
- Adjustment of the wax injection tool and wax injection process to improve fill and achieve target dimensions.
- Polishing of the tool cavities to improve fill and surface finish.
- Investment casting of wax patterns from the modified wax injection tool and measurement of the final casting dimensions.
PLASTIC INJECTION TOOLING
is used when rapid prototypes or wax injection tooling cannot produce suitable patterns for investment casting. Plastic injection tooling is typically fabricated from aluminum or steel and usually requires a base assembly (typically a Master Unit Die or MUD) for operation. The design and fabrication of a plastic injection tool and development of a final injected plastic pattern follows the typical process outlined above for a wax injection tool and may include several tooling and casting adjustments to achieve tight tolerance requirements when specified for precision castings.
RAPID METAL PROTOTYPES
RapidProtoCasting embeds the rapid prototype, wax, plastic or metal patterns in high-temperature industrial refractories. High temperature industrial furnaces cure the refractory materials, producing a ceramic mold that precisely replicates fine detail, thin sections, undercuts, radii and lettering of the pattern. High-strength medical and aerospace alloys are vacuum induction melted and poured into the ceramic molds producing a dense dimensional casting often requiring little finishing or post-processing.